ethereum blockchain protocol An Insightful Overview
Beginning with ethereum blockchain protocol, the narrative unfolds in a compelling and distinctive manner, drawing readers into a story that promises to be both engaging and uniquely memorable.
Ethereum has revolutionized the concept of blockchain by introducing a platform for decentralized applications and smart contracts. Unlike traditional blockchain systems, Ethereum allows developers to build versatile and innovative applications, making it a cornerstone of the blockchain ecosystem. Its architecture and underlying principles establish it as a unique player in the space.
Introduction to Ethereum Blockchain Protocol
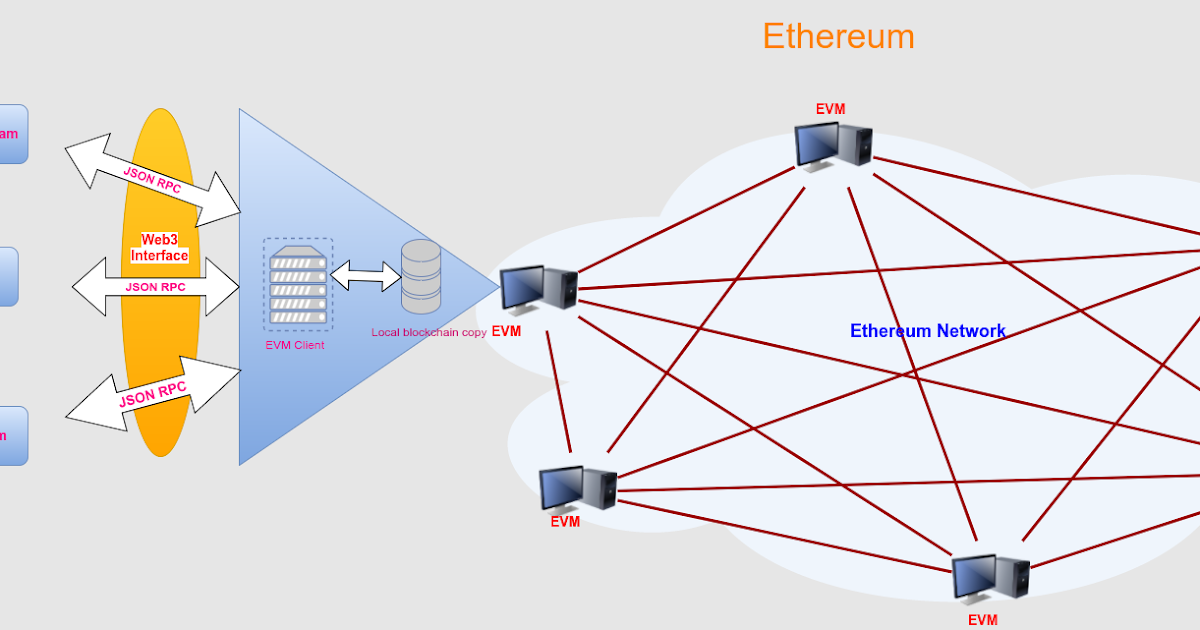
Ethereum is not just a cryptocurrency; it's a groundbreaking blockchain protocol that introduces a decentralized platform for building applications. At its core, blockchain technology revolutionizes how data is stored and shared, ensuring transparency and security through a distributed ledger. Ethereum expands on the traditional concept of blockchain by integrating smart contracts—self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code.
This unique feature substantially differentiates Ethereum from other blockchain frameworks, such as Bitcoin, which primarily focuses on peer-to-peer transactions.The foundational principles of Ethereum revolve around decentralization, immutability, and programmability. Unlike Bitcoin's singular focus on currency, Ethereum offers a versatile platform where developers can create a myriad of decentralized applications (DApps). Its architecture comprises several critical components, including nodes, the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), and the blockchain itself, all of which work together to facilitate the execution of smart contracts and maintain the network's integrity.
Technical Aspects of Ethereum
Understanding the technical aspects of Ethereum sheds light on its operational dynamics and capabilities. The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) serves as a crucial component for executing smart contracts within the Ethereum ecosystem. The EVM is a decentralized execution environment that ensures code runs as intended across all network nodes, providing a secure platform for DApps.Ethereum utilizes different consensus mechanisms to validate transactions and secure the network.
Initially, it operated on proof-of-work (PoW), where miners solved complex mathematical problems to add blocks to the blockchain. However, Ethereum has been transitioning to proof-of-stake (PoS), an energy-efficient mechanism that allows validators to create new blocks based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to "stake" as collateral.The structure of Ethereum blocks and transactions plays a pivotal role in the network’s efficiency.
Each block contains a list of transactions, and users must pay gas fees—transaction fees that incentivize miners and validators to process transactions. These fees can fluctuate based on network congestion, influencing transaction speeds and overall user experience.
Smart Contracts and DApps
Smart contracts are fundamental to the Ethereum blockchain, allowing for automated execution of agreements without the need for intermediaries. They bring numerous advantages, including increased efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced security by eliminating human error. By writing legal agreements in code, smart contracts ensure that terms are enforced exactly as intended.Numerous decentralized applications (DApps) have emerged from the Ethereum platform, each serving unique purposes.
For instance, platforms like Uniswap facilitate decentralized trading of cryptocurrencies, while others, like Aave, focus on lending and borrowing within the DeFi space. NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) have also gained immense popularity, showcasing digital ownership of art and collectibles.Developers can create and deploy smart contracts using the Solidity programming language, a contract-oriented language designed specifically for Ethereum. Solidity's syntax is similar to JavaScript, making it accessible for developers familiar with web development.
This ease of use contributes to the rapid growth of the Ethereum ecosystem, empowering developers to innovate within the blockchain space.
Security and Challenges

Security is a paramount concern within the Ethereum ecosystem, particularly concerning smart contracts. Common vulnerabilities include reentrancy attacks, integer overflows, and improper access control. Developers can mitigate these risks by utilizing best practices such as extensive testing, audits, and formal verification of smart contracts.Scalability remains a challenge for Ethereum, particularly as adoption increases. The network has faced congestion issues, leading to high gas fees and slower transaction times.
Various solutions have been proposed, including Layer 2 solutions like Optimistic Rollups and zk-Rollups, which aim to offload transactions from the main chain to enhance throughput without compromising security.Regulatory challenges also pose significant implications for Ethereum and similar protocols. As governments worldwide begin to scrutinize cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology, compliance will be essential for fostering mainstream adoption. The evolving regulatory landscape could influence how Ethereum operates, impacting everything from transaction processes to the development of DApps.
Future Developments in Ethereum

The roadmap for Ethereum is geared towards continued improvement and adaptation to emerging challenges. Upcoming upgrades, such as Ethereum 2.0, are expected to enhance scalability, security, and sustainability. These upgrades will transition the network fully to proof-of-stake, reducing energy consumption and improving transaction speeds.The ecosystem surrounding Ethereum is rapidly evolving, particularly in the realms of DeFi and NFTs. Decentralized finance platforms are revolutionizing how financial services operate by enabling peer-to-peer lending, borrowing, and trading without intermediaries.
Likewise, NFTs have transformed the digital art landscape, allowing creators to monetize their work in groundbreaking ways.Community governance plays a vital role in shaping the future of the Ethereum blockchain. Developers, stakeholders, and users contribute to discussions surrounding protocol upgrades and modifications, ensuring that the network continues to align with the needs and values of its community. This collaborative approach fosters innovation while maintaining the decentralized ethos that Ethereum is built upon.
Outcome Summary
In summary, the Ethereum blockchain protocol stands at the forefront of technological advancement, bridging the gap between decentralized finance and smart contract functionality. As it continues to evolve, Ethereum's potential for innovation remains vast, promising to shape the future of digital interactions in unprecedented ways.
FAQ Guide
What is the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)?
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is a runtime environment for executing smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain, enabling developers to deploy decentralized applications.
How does Ethereum's consensus mechanism work?
Ethereum primarily uses proof of work (PoW) and is transitioning to proof of stake (PoS), which allows validators to confirm transactions and create new blocks based on their stake in the network.
What are gas fees in Ethereum?
Gas fees are transaction fees paid by users to compensate for the computational energy required to process and validate transactions and smart contracts on the Ethereum network.
What programming language is used for Ethereum smart contracts?
Smart contracts on Ethereum are primarily written in Solidity, a contract-oriented programming language designed specifically for developing applications on the Ethereum platform.
What are Layer 2 solutions?
Layer 2 solutions are protocols built on top of the Ethereum blockchain to improve scalability and transaction speeds by processing transactions off the main Ethereum chain.